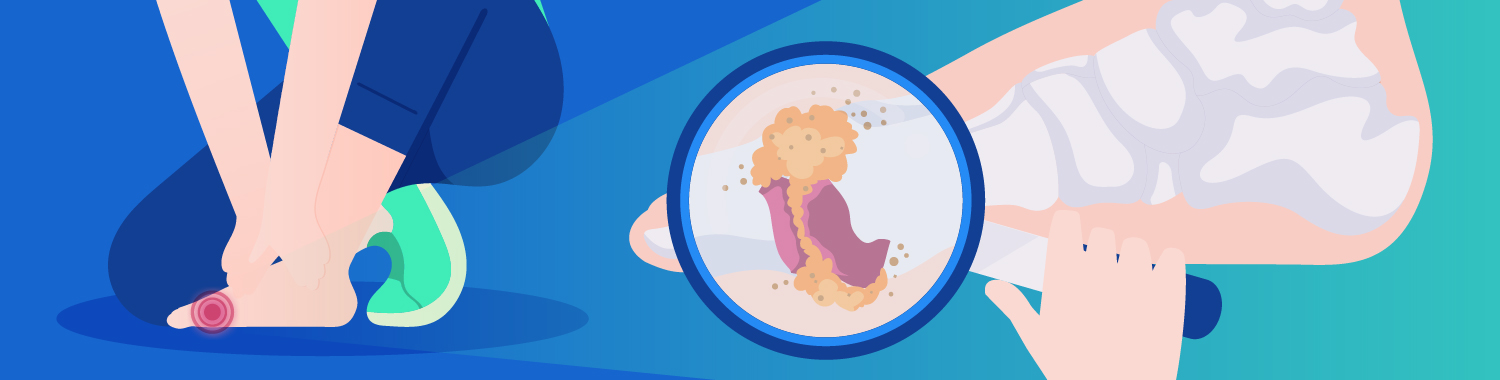
Anyone can be affected by Gout. While there is no cure for it, the best way to treat or prevent it to worsen is to be informed about what it is and what precautionary measures you can take.
What is gout?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis that causes extreme pain and usually affects one joint at a time. The inflammation is mainly caused by a condition known as hyperuricemia, meaning there is a high level of uric acid in one’s body. Due to the excessive uric acid levels found in the body, uric acid crystals (monosodium urate) can build up and form on joints, fluids, or tissues in the body.
When not treated properly, symptoms of it can escalate, which is known as gout flares. Repeated flares can lead to Gouty arthritis, a worsening form of arthritis.
What are the signs and symptoms of gout?
Gout can come and form at any time, even when sleeping. The first feeling that is reported when experiencing a gout flare, is the sensation of one of your joints burning. Here are the symptoms you need to look out for when experiencing a similar feeling in your joints:
- Intense pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Redness
- Tenderness
- Affected joint is warm to touch
Attacks or flares can last from days to a week or two. In between flares, symptoms of gout abate, which is known as a remission period.
How does an individual get gout?
Genetic and environmental factors contribute to one’s predisposition in developing Gout.
A positive family history of Gout and having a condition involving genes that control the urate transporters (causing one’s inability to excrete urate in the urine leading to urate build-up in the body) are the genetic components.
Age and sex also play a role. It occurs more in men between ages 30 to 50 years old. Women develop signs and symptoms of Gout generally after menopause.
Meanwhile, environmental factors are often due to one’s unhealthy lifestyle. The following factors contribute to Gout development:
Diet
High intake of animal protein, especially red meat and organ meats; consumption of significant amount of alcohol; drinks high in fructose
Obesity
The body produces more uric acid when a person is overweight or obese.
Medical Conditions
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Poor Kidney function
- Insulin Resistance
How can individuals manage and prevent it?
There is no active cure for gout. However, there are treatments and strategies you can lean on to manage its symptoms.
- Have a healthy diet. Avoid foods that may help trigger and develop a gout flare such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood. Avoiding excessive alcohol intake and rather lean on to drinking plenty of water can also improve one’s kidneys’ function better.
- Manage the pain of a flare. There are certain medicinal treatments you can take to ease the symptoms such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, steroids, and colchicine.
- Prevent the formation of tophi and kidney stones. Tophi are hard, uric acid deposits under the skin, mainly developed through chronic high levels of uric acid. Doctors mainly recommend taking preventive therapy through the use of drugs like Allopurinol and Febuxostat.
If you think you might have gout and its symptoms, please do not hesitate to call a doctor. Our specialist doctors here at Medgate are very much ready to help you and diagnose your case. Do not hesitate to give us a call before it’s too late.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4755-gout
https://www.healthline.com/health/gout/is-gout-hereditary
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gout/symptoms-causes/syc-20372897
